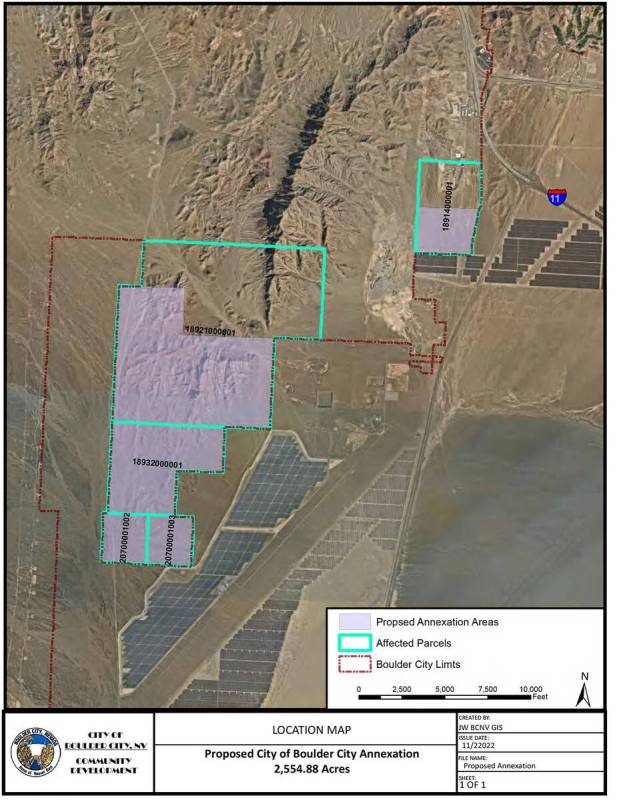
The City Council voted unanimously Tuesday, Feb. 14, to begin the process of annexing some 2,550 acres of land in the Eldorado Valley. The vote sets up a process that will continue with the council hearing public comment at its meeting scheduled for March 28.
The annexation would be the end result of negotiations between Boulder City and Henderson over the status of land that lies between the boundaries of the two municipalities but that is in unincorporated Clark County. If the annexation is approved, it would solidify the boundaries between the two cities, said City Manager Taylour Tedder in a presentation to the council.
“This action would largely eliminate any unincorporated land between Boulder City and Henderson with more than 95 percent of the surrounding land being within the city limits of either Boulder City or Henderson,” he said.
The land in question is owned by the Bureau of Land Management and annexation would not change that status. It would, however, make any future use of the land subject to zoning and permitting rules in Boulder City. The land to be annexed is not slated for development.
Future use for the great majority of the acreage is intended to be limited to providing open space and the move was described by council members as setting up a kind of buffer zone between Boulder City and Henderson. Even if the land were to be used for a purpose, such as expanding the current solar facility — which has been proposed and may happen on a small 80-acre plot — any revenue from that use would go to the BLM and not contribute to Boulder City’s budget. Tedder noted that while no revenue would be derived from the land, the city would benefit by having a voice in that development via zoning and permitting.
Earlier in the meeting, the council heard a presentation from Utilities Director Joseph Stubitz about the current state of public utilities in the city. With the exception of natural gas service, most utilities, i.e., water, electric, wastewater and solid waste services, are city owned and not for profit.
Of greatest note were wastewater and the rising costs of electricity.
According to Stubitz, the city treats 1,288 acre-feet — or about 400 million gallons — of wastewater every year. After treatment, that water is stored in evaporation pools where it eventually dissipates. This is in contrast to the system in the Las Vegas Valley that treats and filters wastewater and returns more than 90 percent of it back to Lake Mead. Because of this recycling, if Nevada’s allotment of Colorado River water is lowered by the federal government as is widely expected, actual water usage would still fall below the official allotment.
Stubitz reported that the price paid for electricity by the city had risen 28 percent in 2022 and was expected to increase by an additional 35 percent this year. Mayor Joe Hardy noted that long-term contracts with power generation companies insulated residents and businesses in the city from some of these rising costs.
“Power costs in Boulder City are still lower than anywhere else in the region,” he said.
Stubitz confirmed this.
Future meetings will include information on plans to update the city’s aging power infrastructure to guard against a future in which decreasing water levels in Lake Mead may lead to less electricity being available from Hoover Dam.
Contact reporter Bill Evans at wevans@bouldercityreview.com or at 702-586-9401.